News
Check out my book with Manning Publications! "Machine Learning for Drug Discovery" is available via Manning's Early Access Program (MEAP)! Check it out here and use code "au35fly" for a 35% discount! Feel free to browse (or contribute) to the official code repository! I've recently released chapter 10 on "Generative Models for De Novo Design" -- happy learning!
I’m thrilled to announce that I’m presenting a short demo at PyTorch Conference, Oct 22-23 in San Francisco! Check out my session, "Designing Medicines from Scratch: PyTorch Workflows for De Novo Drug Discovery", and explore the schedule.
Bio
As an Applied Scientist at AWS Agentic AI, I specialize in developing scalable and robust artificial intelligence systems. My work involves repurposing foundation models for improved domain adaptation and long context reasoning, building customizable multi-agent frameworks that reduce development time and primitives that generalize across multiple verticals (deep research, coding, data science), and improving agentic evaluation processes for greater customization and personalization. I am also interested in mixture-of-agents and parameter-efficient reinforcement learning.
Previously, I was a Research Scientist with Amazon's Alexa & AGI team , where I contributed to the Amazon Nova model family. There, I focused on enhancing tool usage capabilities and developing dynamic data selection strategies for multilingual expansion, all while owning experimentation and production model release cycles.
My background is rooted in the intersection of deep learning and drug discovery, which was the focus of my PhD at Washington University in St. Louis and the subject of my book, "Machine Learning for Drug Discovery" -- Check it out!. The search for novel, improved therapeutics is an important problem and impacts all of our lives. "Machine Learning for Drug Discovery" is an informative deep dive that aligns machine learning and deep learning theory with contemporary applications in drug discovery. While a cliché, it is nevertheless true: this is the book I wish I had available to me when I started my graduate studies and early career in industry. Each chapter is structured around real-world scenarios and iteratively builds up a solution with code provided every step of the way. By the end, you'll have the agency to explore, apply, replicate, and improve upon innovations and publications at the intersection of machine learning and drug discovery. Both seasoned researchers and newcomers welcome -- no prior background in chemistry or machine learning is necessary!
My doctoral research involved modeling drug metabolism networks using graph neural networks to predict drug toxicity and applying machine learning to electronic health records to predict drug-induced liver injury and drug-drug interactions. As part of my research, I served as a core maintainer of XenoSite and I launched the XenoNet Web Server. I remain connected to the academic community as an Adjunct Instructor at the University of California, Berkeley , where I develop and teach graduate-level courses in machine learning and cheminformatics.
I'm always interested in connecting with others who are passionate about building impactful technology. Please feel free to reach out to discuss agentic AI, computational drug discovery, or potential collaborations.
Publications
Most recent publications on Google Scholar.
‡ indicates equal contribution.
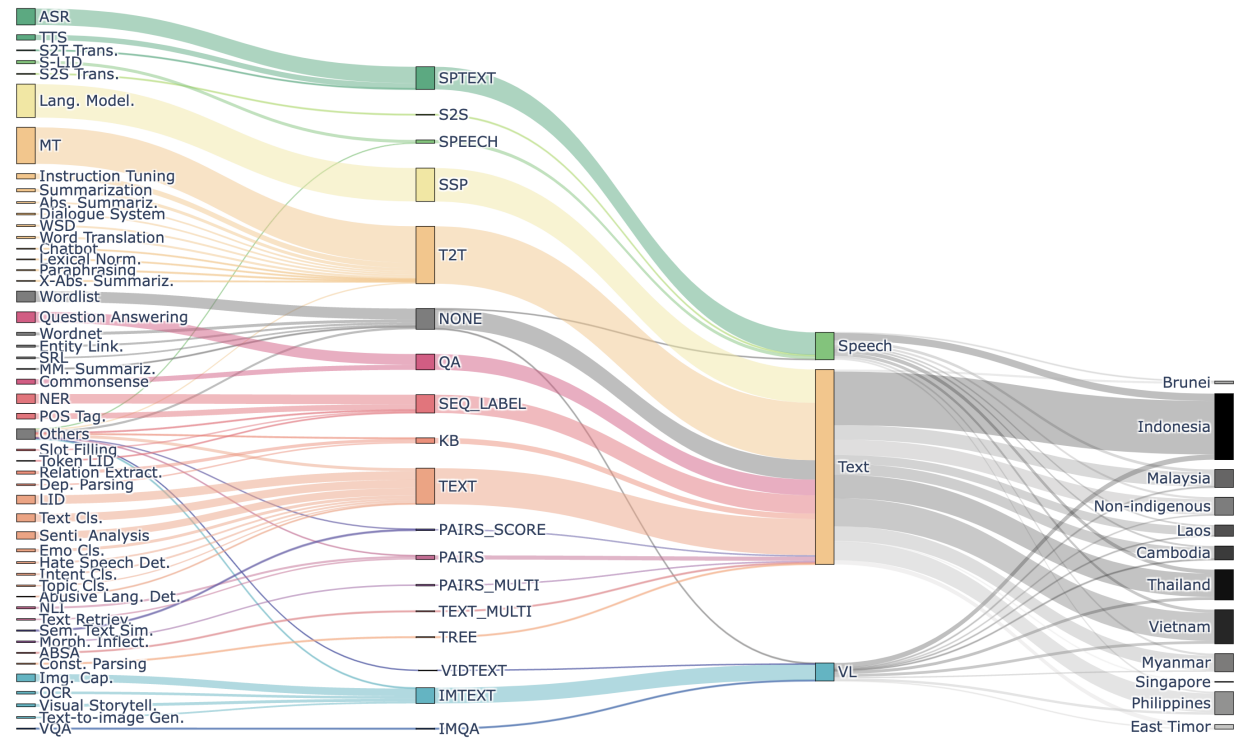
SEACrowd: A Multilingual Multimodal Data Hub and Benchmark Suite for Southeast Asian Languages
Holy Lovenia, et al. (including Noah R. Flynn)
EMNLP (2024)
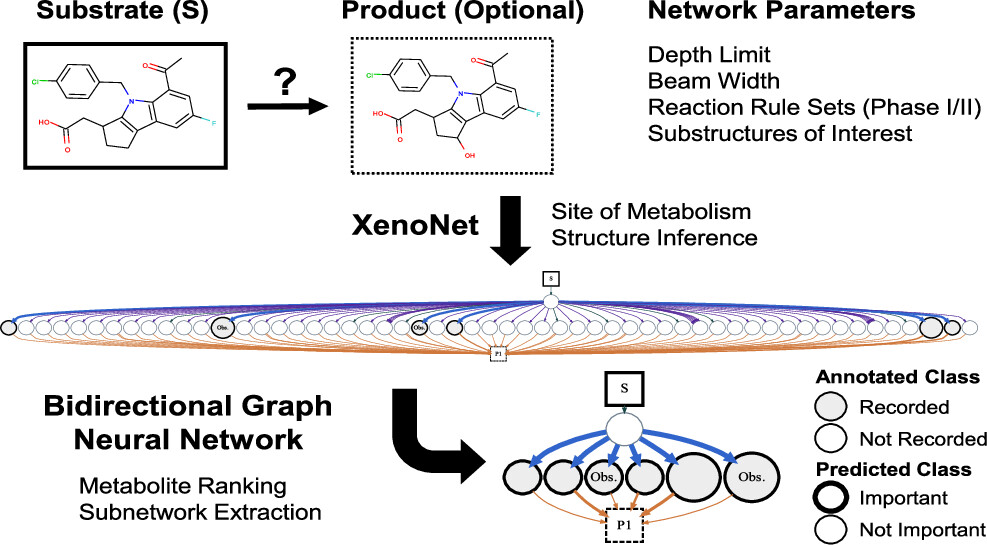
Message Passing Neural Networks Improve Prediction of Metabolite Authenticity
Noah R Flynn, S Joshua Swamidass
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (2023)
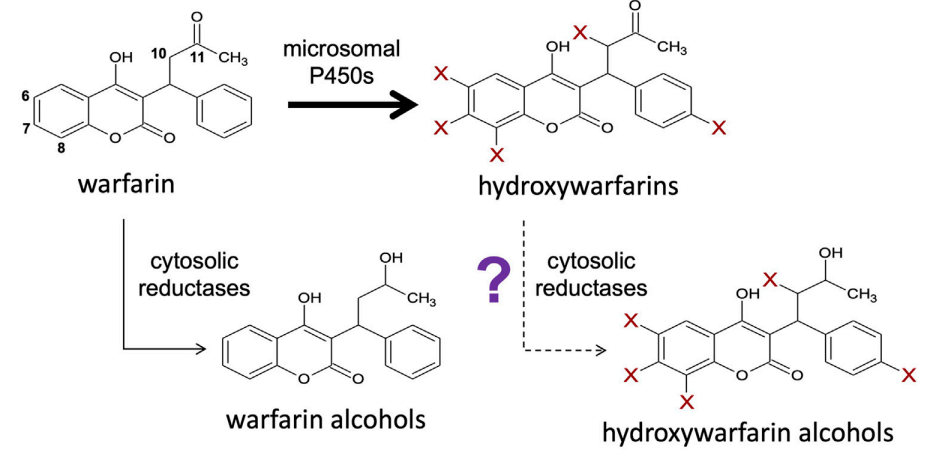
Discovery of Novel Reductive Elimination Pathway for 10-Hydroxywarfarin
Dakota L Pouncey, et al. (including Noah R Flynn)
Frontiers in Pharmacology (2022)
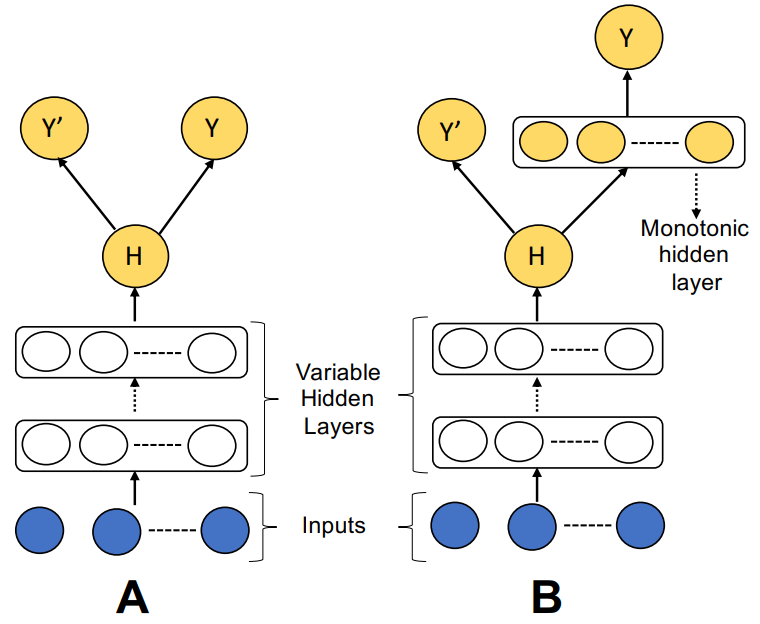
Cal-net: Jointly learning classification and calibration on imbalanced binary classification tasks
Arghya Datta, Noah R Flynn, S Joshua Swamidass
IJCNN (2021)
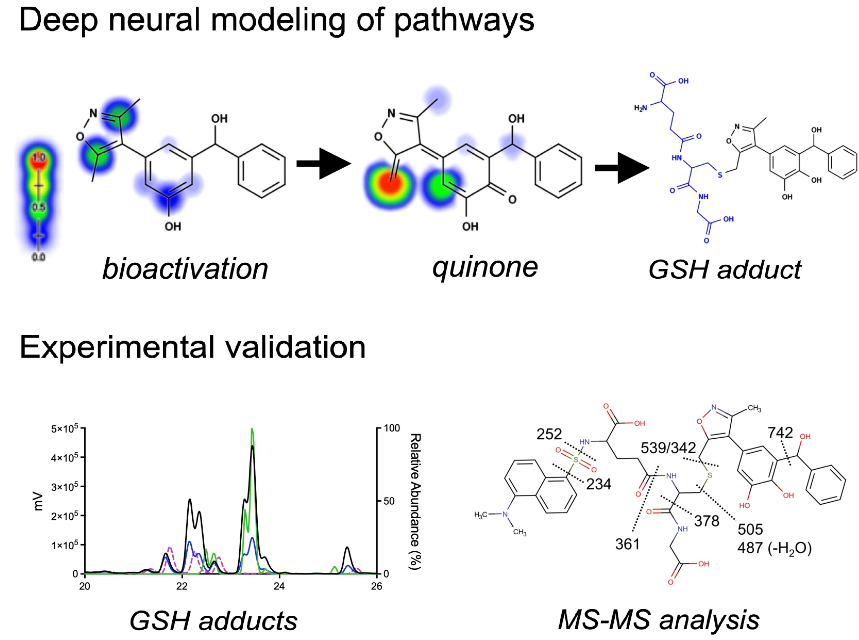
Bioactivation of Isoxazole-Containing Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibitors
Noah Flynn, Michael D. Ward, Mary A. Schleiff, et al.
Metabolites (2021)
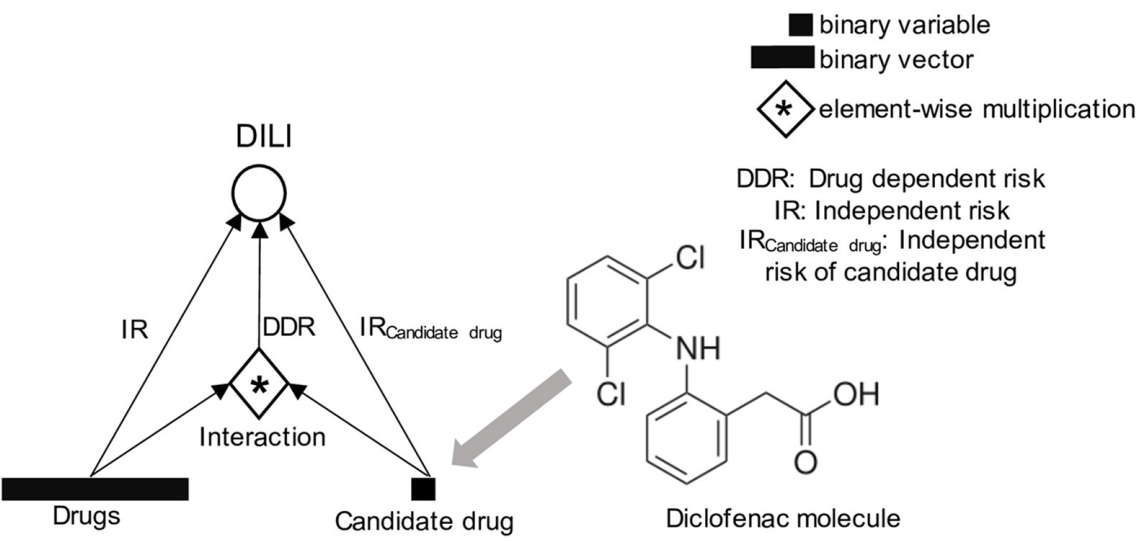
Machine Learning on Liver-Injuring Drug Interactions with NSAIDs from Hospitalization Data
Arghya Datta‡, Noah Flynn‡, Dustyn A Barnette, et al.
PLOS Computational Biology (2021)
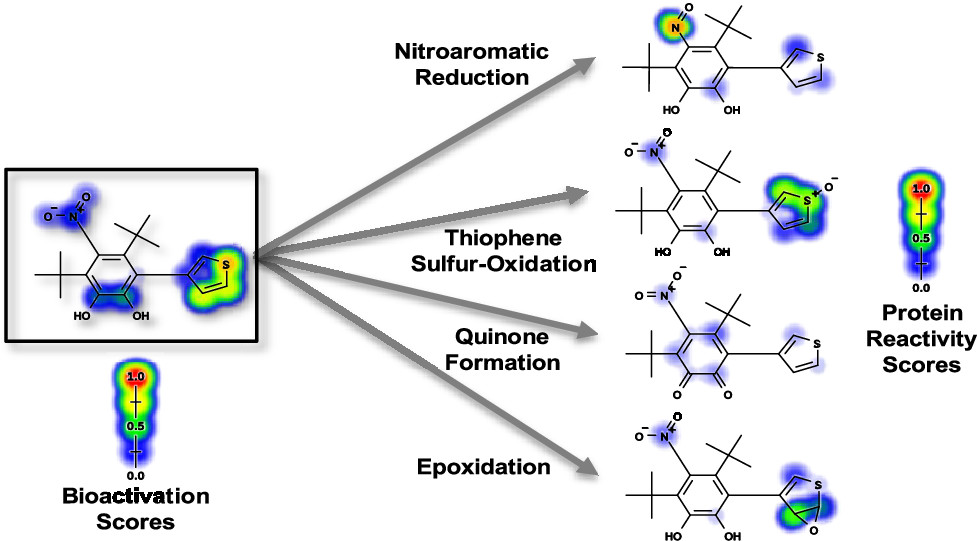
Modeling the Bioactivation and Subsequent Reactivity of Drugs
Tyler B Hughes‡, Noah Flynn‡, Na Le Dang, S Joshua Swamidass
Chemical Research in Toxicology (2021)
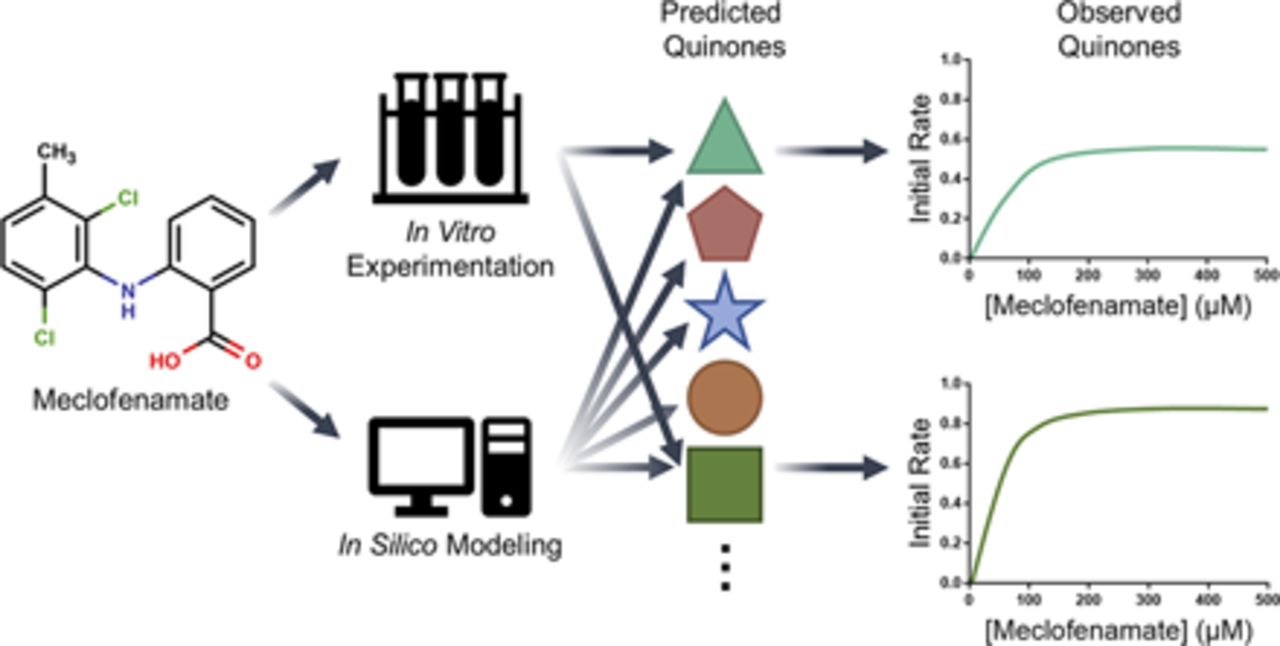
Significance of Multiple Bioactivation Pathways for Meclofenamate as Revealed through Modeling and Reaction Kinetics
Mary A Schleiff, Noah R Flynn, Sasin Payakachat, et al.
Drug Metabolism and Disposition (2021)
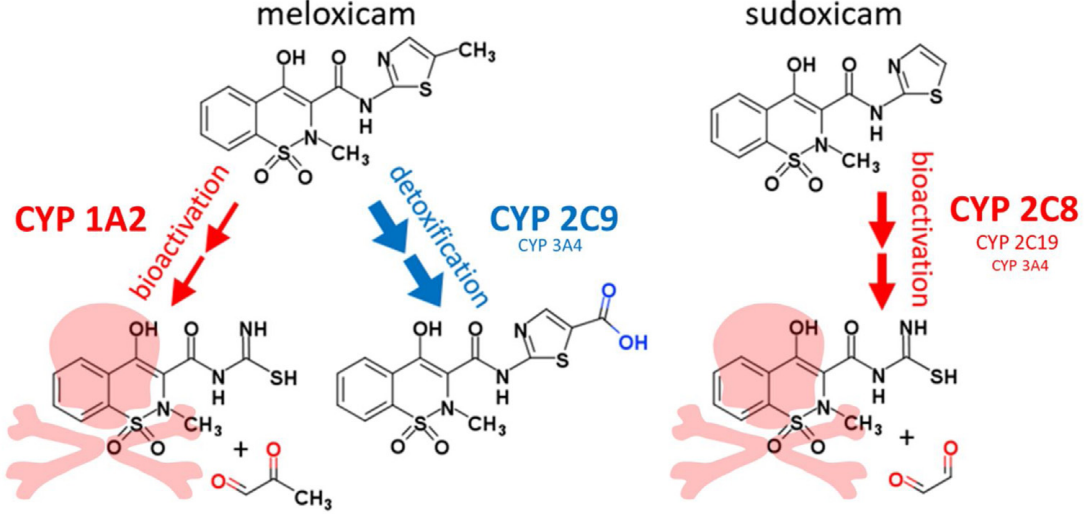
Meloxicam methyl group determines enzyme specificity for thiazole bioactivation compared to sudoxicam
Dustyn A Barnette, et al. (including Noah Flynn)
Toxicology Letters (2020)
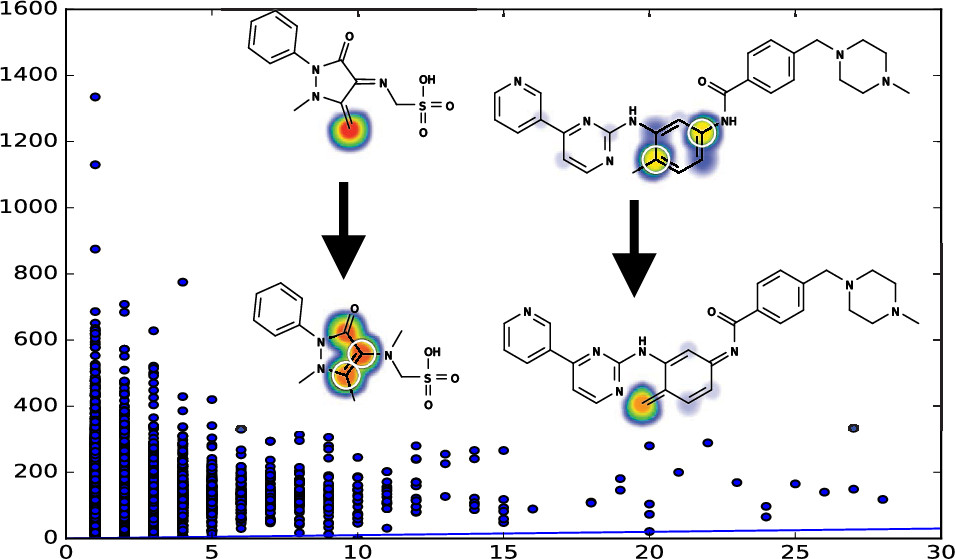
The Metabolic Forest: Predicting the Diverse Structures of Drug Metabolites
Tyler B Hughes, Na Le Dang, Ayush Kumar, Noah R Flynn, S Joshua Swamidass
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (2020)
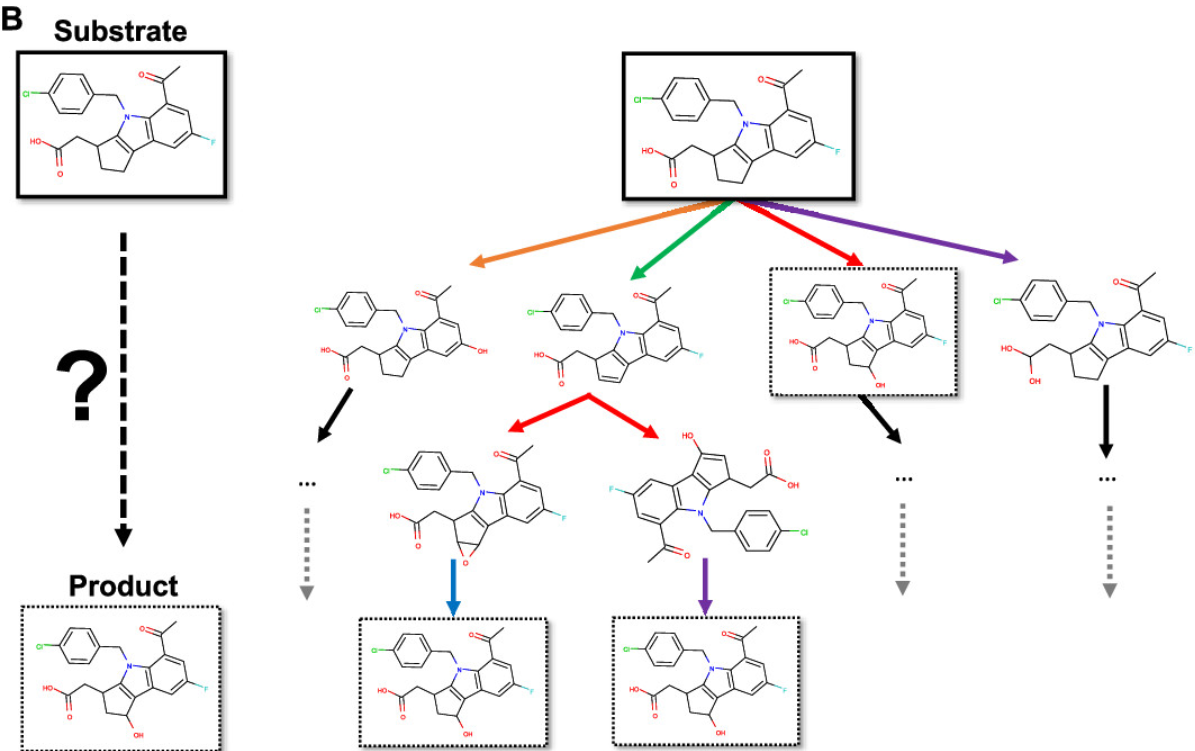
XenoNet: Inference and Likelihood of Intermediate Metabolite Formation
Noah R Flynn, Na Le Dang, Michael D Ward, S Joshua Swamidass
J. of Chem. Inf. Model. (2020)
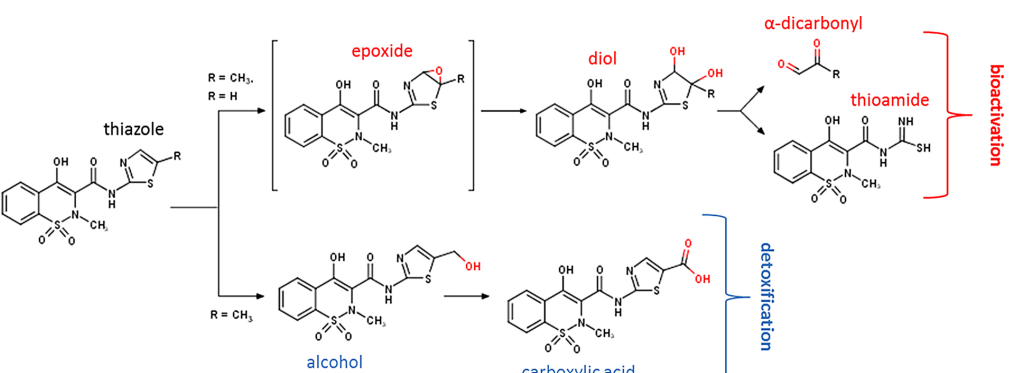
Dual mechanisms suppress meloxicam bioactivation relative to sudoxicam
Dustyn A Barnette, et al. (including Noah Flynn)
Toxicology (2020)
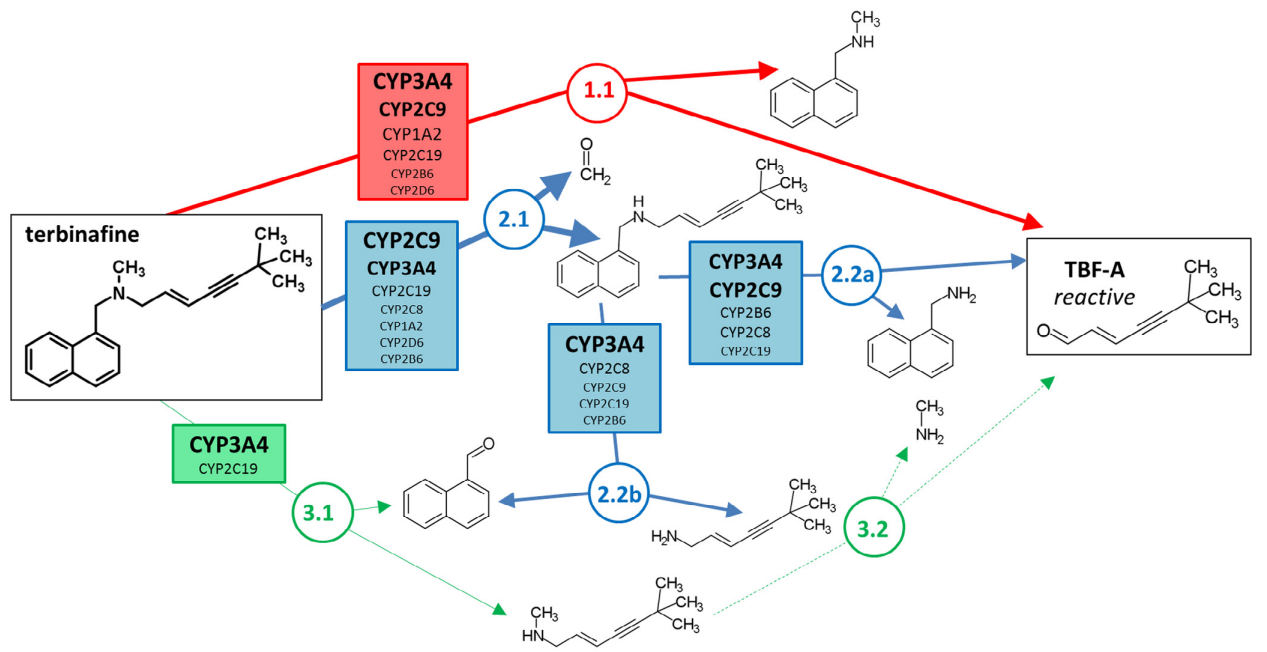
Comprehensive kinetic and modeling analyses revealed CYP2C9 and 3A4 determine terbinafine metabolic clearance and bioactivation
Dustyn A Barnette, Mary A Davis, Noah Flynn, et al.
Biochem. Pharmacol. (2019)
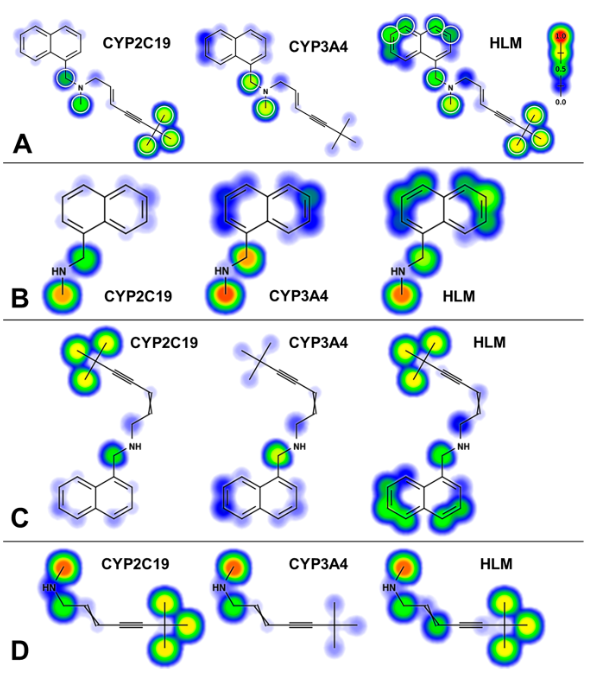
CYP2C19 and 3A4 Dominate Metabolic Clearance and Bioactivation of Terbinafine Based on Computational and Experimental Approaches
Mary A Davis, Dustyn A Barnette, Noah R Flynn, et al.
Chemical Research in Toxicology (2019)

Message Passing Neural Networks Improve Prediction of Metabolite Authenticity
Noah R Flynn, S Joshua Swamidass
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (2023)

Cal-net: Jointly learning classification and calibration on imbalanced binary classification tasks
Arghya Datta, Noah R Flynn, S Joshua Swamidass
IJCNN (2021)

Bioactivation of Isoxazole-Containing Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibitors
Noah Flynn, Michael D. Ward, Mary A. Schleiff, et al.
Metabolites (2021)

Machine Learning on Liver-Injuring Drug Interactions with NSAIDs from Hospitalization Data
Arghya Datta‡, Noah Flynn‡, Dustyn A Barnette, et al.
PLOS Computational Biology (2021)

Modeling the Bioactivation and Subsequent Reactivity of Drugs
Tyler B Hughes‡, Noah Flynn‡, Na Le Dang, S Joshua Swamidass
Chemical Research in Toxicology (2021)

XenoNet: Inference and Likelihood of Intermediate Metabolite Formation
Noah R Flynn, Na Le Dang, Michael D Ward, S Joshua Swamidass
J. of Chem. Inf. Model. (2020)
Vitæ
Full Resume in PDF.
-
UC Berkeley Jun 2024 - nowAdjunct Faculty
Molecular Science & Software Engineering -
Amazon Sep 2024 - nowApplied Scientist II
AWS AI Labs -
Amazon Jun 2021 - Sep 2024Research Scientist II
Alexa AI & AGI -
Merck (MSD) May 2019 - Aug 2019Machine Learning Intern
Modeling & Informatics -
WUSTL Aug 2017 - Jun 2021Ph.D. Student
Computational Biology
Department of Pathology & Immunology -
National Center for Supercomputing Applications May 2016 - May 2017Computational Research Fellow
-
UIUC College of Engineering Apr 2016 - Jul 2017Director
Engineering Open House -
AbbVie Nov 2015 - May 2017Software Engineer, Intern
Platform Informatics & Knowledge Management -
Seitz Materials Research Lab Dec 2014 - Aug 2016Research Assistant
John Rogers Group -
Institute for Genomic Biology Feb 2014 - Sep 2015Research Assistant
Biosystems Design Group (iGEM) -
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2013 - 2017B.Sc. Student
Bioengineering
Computer Science (Minor)
